-
Article
- GPU-Accelerated Optimal Interpolation for Global Ocean Surface pCO2 Mapping
- Gyundo Pak
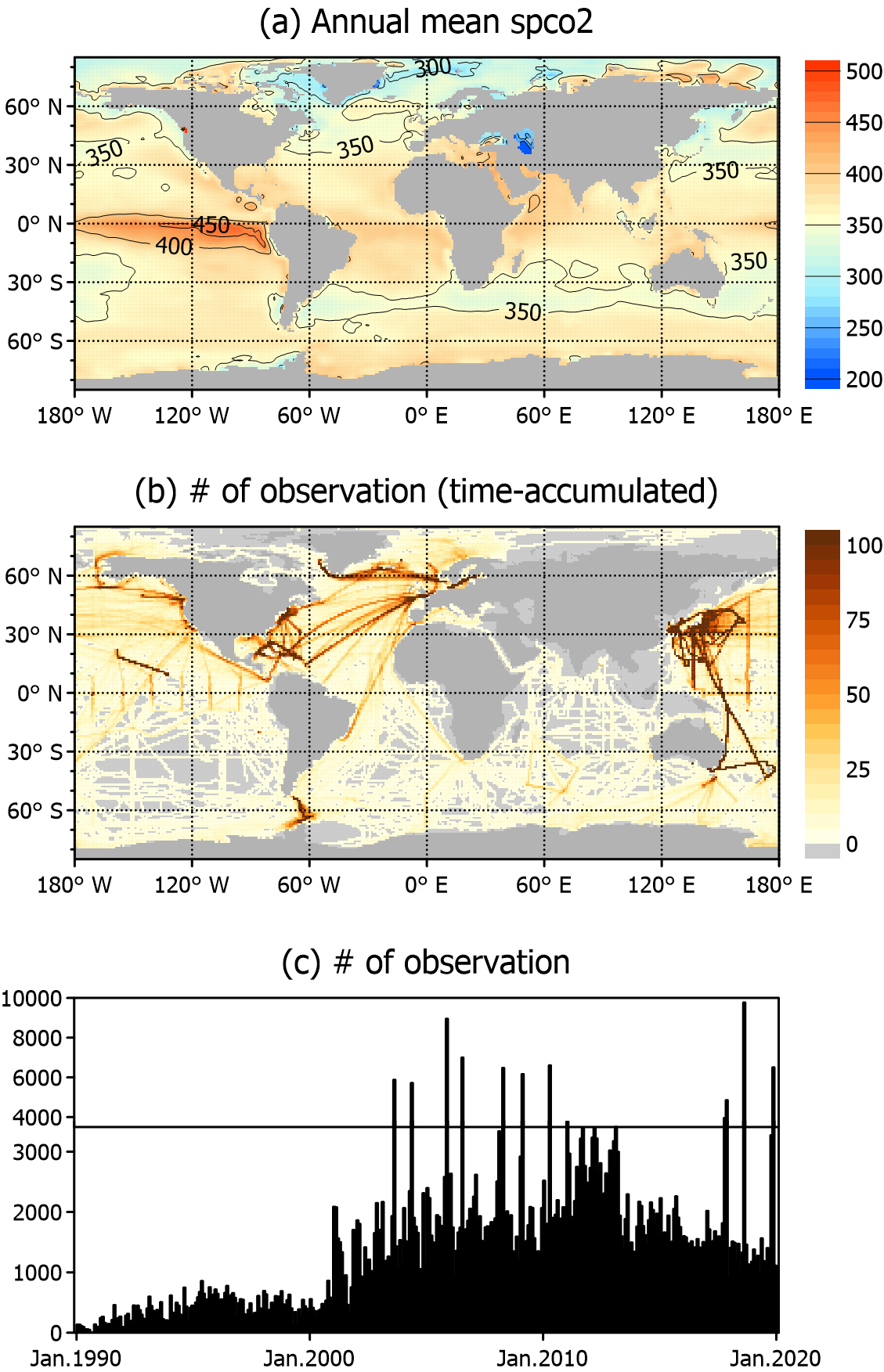
- GPU acceleration has become essential for meeting the rising computational demands of high-resolution ocean modeling and data assimilation. In this study, a …
- GPU acceleration has become essential for meeting the rising computational demands of high-resolution ocean modeling and data assimilation. In this study, a GPU-accelerated, chunk-based, sequential Optimal Interpolation (OI) scheme was developed to reconstruct global ocean surface partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2) fields. OI analyses were successfully performed for the period between 1990 and 2019 using 30 years of monthly background fields and observations. Benchmarking highlighted substantial gains, with runtimes up to 35 times faster than that of a single-core CPU baseline and approximately 12 times faster than that of multi-core CPU runs. The GPU performance improved steadily with increasing chunk size, whereas the fastest runtimes were consistent with observation batch sizes in the range of 1,000–2,000. Sequential OI generated analysis fields nearly identical to those from the all-at-once observation update, and its runtime ranged from a bit slower to slightly faster depending on the choice of observation batch size. These results show that GPU-based OI is both practical and efficient, offering a pathway for the direct application of GPUs in operational ocean prediction systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Article
-
Study on Performance Improvement of a Flapping-foil Hydrokinetic Turbine of Parallel Configuration
진동익 유체동력 터빈의 병렬 배치에 따른 성능 향상 연구
-
Sang Chul Lee, Dasom Jeong, Jin Hwan Ko
이상철, 정다솜, 고진환
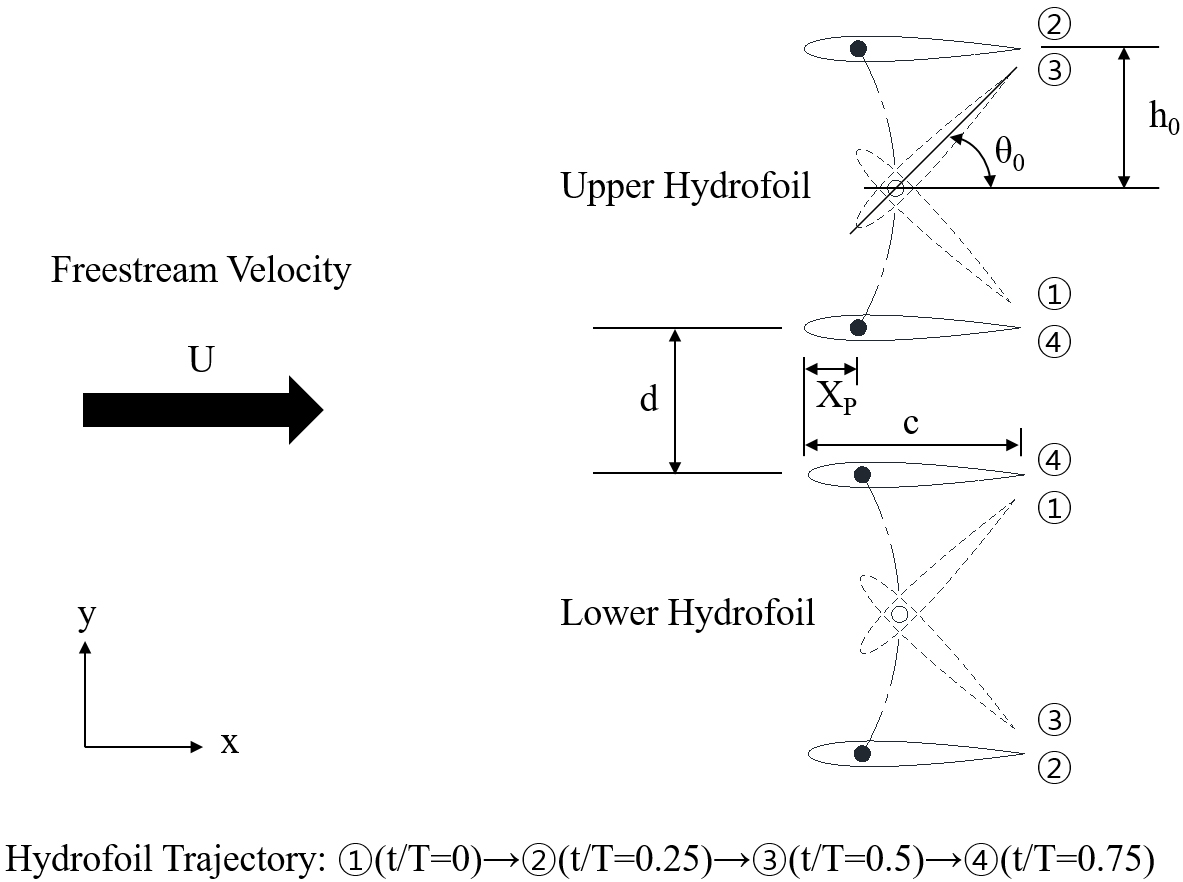
- In this study, we performed 2D simulations with varying separation distances to determine the influence of ground effect on the efficiency of …
- In this study, we performed 2D simulations with varying separation distances to determine the influence of ground effect on the efficiency of parallel-configured flapping-foil hydrokinetic turbine. The efficiency was highest at 38.38% in the case of the closest distance (d/c = 2.0), which was 2.32% higher than the case of the farthest distance (d/c = 4.0) and 10.49% higher than the case of a single turbine. In all cases, lift contributed the most to the power, at over 80%, and moment contributed mainly in the phase where the direction of heave motion changed. The increase in efficiency due to ground effect occurs mainly in the leaving phase, and the pressure increase on the lower surface due to the blockage effect and the pressure decrease due to the leading edge vortex on the upper surface were the main causes in the early and later stages, respectively. - COLLAPSE
-
Study on Performance Improvement of a Flapping-foil Hydrokinetic Turbine of Parallel Configuration



 Ocean and Polar Research
Ocean and Polar Research








